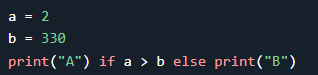
Python If ... Else
Python Conditions and If statements
Python supports the usual logical conditions from mathematics:
- Equals: a == b
- Not Equals: a != b
- Less than: a < b
- Less than or equal to: a <= b
- Greater than: a > b
- Greater than or equal to: a >= b
These conditions can be used in several ways, most commonly in "if statements" and loops.
An "if statement" is written by using the if
keyword.
Example
If statement:
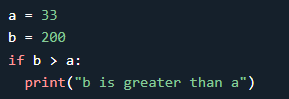
In this example, a and b are compared to check if a is greater
than b. If true, the statement inside the if block is executed.
Indentation
Python relies on indentation (whitespace at the beginning of a line) to define scope in the code. Other programming languages often use curly-brackets for this purpose.
elif
The elif keyword is Python's way of saying "if the
previous conditions were not true, then try this condition".
Example
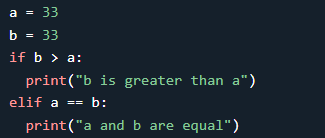
In this example, the first condition is not true. The next
condition (elif) is true, so the code in the elif block is executed.
Else
The else keyword catches anything which isn't
caught by the preceding conditions.
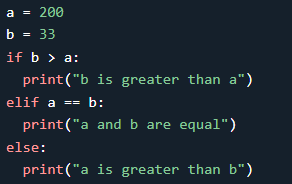
If you have only one statement to execute, you can put it on the
same line as the if statement.
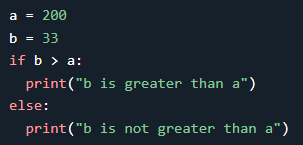
In this example, since a is greater than b, the first condition
is not true, the elif condition is also not true, so we go to the else
condition and print "a is greater than b" to the screen.
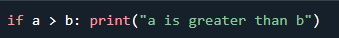
Short hand IF
If you have only one statement to execute, you can put it on the
same line as the if statement.
Short Hand If ... Else
If you have only one statement to execute for if,
and one for else, you can put it all on the same line: